Subproject 4: 4: Staphylococcus aureus-induced microenvironments in premature babies, neonatals and toddlers and its role in neoplasia
University Children´s Clinic: Jorch G
Experimental Pediatrics: Brunner-Weinzierl MC
Staphylococcus aureus (S. aureus) is often found in antibiotic-resistant strains (Methicillin-resistant S. aureus). It plays a role in sepsis and when it colonizes a child’s intestines early, it is correlated with later development of allergies. It is also correlated with cancers (among others T-cell lymphoma) and with pediatric cancer patients with complications and a higher mortality rate. Because neonatals and toddlers are especially vulnerable to infections, a basic understanding of the role of S. aureus especially with regard to age-dependent differences is important in order to develop new treatment strategies.
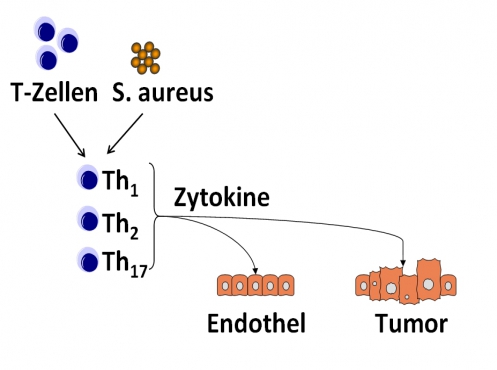 |
|
Figure: Schematic representation of the project. T-cells from neonatals, toddlers and adults are stimulated with S. aureus and its effector functions, polyfunctionality and homeostasis are analyzed in detail. For this, Q-PCR and flow cytometry among other tests were carried out using a Boolean gating. |






